Charlie Gard Post-Mortem: Could He Have Been Saved?
Charlie Gard would have turned one year old tomorrow.
Two days before the British infant died of a mitochondrial disease on July 28, a short article in MIT Technology Review teased that Shoukhrat Mtalipov and his team at Oregon Health & Science University and colleagues had used CRISPR-Cas9 to replace a mutation in human embryos, a titillating heads-up that didn’t actually name the gene or disease.
Yesterday Nature published the details of what the researchers call gene correction, not editing, because it uses natural DNA repair. I covered the news conference, with a bit of perspective, for Genetic Literacy Project.
Might gene editing enable Charlie’s parents, who might themselves develop mild symptoms as they age, to have another child free of the family’s disease? Could anything have saved the baby?
A TRAGIC CASE
The court hearing testimony on the case between Great Ormond Street Hospital (GOSH) and the family, published April 11, chronicles the sad story. The hospital had requested discontinuing life support based on the lack of tested treatment.
 Charlie was born August 4, 2016, at full term and of a good weight, but by a few weeks of age, his parents noticed that he could no longer lift his head nor support any part of his body. By the October 2 pediatrician visit, Charlie hadn’t gained any weight, despite frequent breastfeeding. After an MRI and EEG, Charlie had a nasogastric tube inserted to introduce high-caloric nutrition.
Charlie was born August 4, 2016, at full term and of a good weight, but by a few weeks of age, his parents noticed that he could no longer lift his head nor support any part of his body. By the October 2 pediatrician visit, Charlie hadn’t gained any weight, despite frequent breastfeeding. After an MRI and EEG, Charlie had a nasogastric tube inserted to introduce high-caloric nutrition.
By October 11, the baby was lethargic, his breathing shallow. So his parents, Connie Yates and Chris Gard, took him to GOSH. There, physicians noted Charlie’s “persistently elevated lactate.” It was an ominous sign.
Remember Bio 101? When cellular respiration in the mitochondria fails, an alternate pathway releases lactic acid – this is what causes muscle cramps in a sprinter right after a race. It’s what was happening to the thousands of mitochondria in Charlie’s muscle cells; they weren’t extracting enough ATP energy from digested nutrients, and so the baby was limp, unable to reach or react much. His brain was running out of energy too.

On October 25, a muscle biopsy indicated only 6% of the normal amount of mitochondrial DNA, well below the 35% that indicates a mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome (MDDS). But which one did Charlie have? Which gene was mutant? That’s important. With a judge discussing “strains” of the syndrome, as if it is a bacterial infection and not a monogenic disease, confusion loomed.
In mid November, sequencing of Charlie’s genome found two mutations in the gene RRM2B, causing “infantile onset encephalomyopathic MDDS.” It affected the brain and muscles – that was obvious – but he was also deaf and had heart and kidney abnormalities. With these findings, the Ethics Committee at GOSH advised against a ventilator.
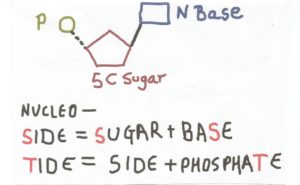
Charlie’s disease is a “block to the machinery in charge of supplying nucleotide building blocks for mitochondrial DNA synthesis,” Fernando Scaglia, professor of medical and human genetics at Baylor College of Medicine, told me when I picked his brain on whether gene editing might help Charlie’s parents.
(A quasi-technical aside: RRM2B encodes an enzyme [ribonucleotide reductase] that, with three other subunits, removes an oxygen from the sugar part of nucleic acid building blocks, leaving deoxyribose as the sugar rather than ribose, with two phosphates attached. This happens just outside the mitochondria. Once these precursors get into the mitochondria, a third phosphate is added, forming the DNA nucleotide building blocks of the 37 mitochondrial genes. Charlie inherited a RRM2B mutation from each parent – the gene is in the nucleus, but it is essential to supply the mitochondria with nucleotides. RRM2B’s enzyme works only in cells that aren’t dividing – hence the extreme effects on Charlie’s muscles and brain.)
Charlie’s seizures started on December 15 and never let up. Experts began weighing in, including by the end of the month Michio Hirano from Columbia University, who had experience using nucleoside bypass therapy on 18 patients with MDDS due to mutations in a different gene, TK2. A ray of hope?
Nucleoside bypass therapy provides precursors to the DNA building blocks that have only one of the three phosphates, to circumvent the disabled enzyme, and because the full forms are too highly charged to easily enter cells. But the paper analyzing the strategy, from 2012, clearly showed that it didn’t work in an experimental system for Charlie’s disease – “myotubes,” bits of non-dividing muscle in a dish:
“First we suggest that not only myotubes (post-mitotic cells), but also myoblasts and possibly other dividing cells can show mtDNA depletion in RRM2B deficiency. Second, supplementation with dNMPs, as expected, had no beneficial effect in RRM2B deficiency. Based on the function of this protein supplementation with dNDPs could be tried as an alternative strategy in RRM2B deficiency.” (This isn’t a sentence, albeit the crucial one for the case; it means trying two phosphates instead of one.)
I’m guessing that these three sentences are what catalyzed the parents’ GoFundMe effort and desire to take their baby to the US. But “there’s never been a proper clinical trial for nucleoside therapy,” said Dr. Scaglia, although 18 patients in Spain and Italy with mutations in a different gene, TK2, have so far tolerated it. But that form only affects muscle. The treatment might not have crossed the blood-brain barrier to reach Charlie’s more extensive disease.
Justice Francis knew the limitations of what some in the media called the “pioneering treatment,” if not the difference between a microbe and a gene. “In fact, this type of treatment has not even reached the experimental stage on mice let alone been tried on humans with this particular strain of MDDS,” he wrote.

(NHGRI)
From January 9th until the 27th, Charlie had an unrelenting storm of seizures, his EEG erratic even when he wasn’t obviously seizing. This setback caused postponement of an ethics committee meeting and all but Dr. Hirano to give up. Perhaps he thought it a “theoretical possibility” because of that one sentence in the 2012 paper that suggested giving DNA precursors with 2 phosphates instead of one.
For a time, Columbia University considered treating Charlie, with what I don’t know. Meanwhile, nurses noted and then testified that the baby was gaining weight but making no obvious progress, countering the parents’ observations that Charlie felt pain, distress, pleasure, and subtly communicated with them.
Then an EEG from March 30 convinced even Dr. Hirano that an attempt at any treatment would be futile – a term that so dominated the court hearing that Justice Francis defined it: “for the avoidance of any doubt, the word “futile” in this context means pointless or of no effective benefit.” Goals began to focus on preventing suffering.
Yet the Pope and the President weighed in circa July 4, offering to welcome the baby for unspecified treatment to the Vatican or US. What did they know that the English doctors didn’t? And I had to wonder, where are these notables when similar things happen to many other babies born with rare genetic diseases? (See No Ice Buckets or Pink Ribbons for Very Rare Genetic Diseases)
For a time, discussion at the hearing devolved into a UK vs US scenario of the Brits taking a more reasoned approach in denying a futile therapy whereas US docs would try anything if parents could just raise enough money.
As the Pope and President were making their kind offers, pretty much all the experts were reaching agreement that Charlie should be taken off life support. Still, and understandably, the parents grabbed at any hope. “We truly believe that these medicines will work,” the father told the court, although nucleoside bypass was more an untested hypothesis than a medicine. Belief can’t alter biochemistry.
And so Charlie passed away on July 28.
COULD ANYTHING HAVED SAVED CHARLIE?
It was too soon for nucleoside bypass therapy, nor were approaches for other mitochondrial diseases such as cofactor supplementation (which I wrote about here), liver transplant, or stem cell transplant applicable. Nor can a recently-described peptide-like molecule that silences mitochondrial genes help, because Charlie’s mutant genes are in the nucleus. (A mitochondrion only houses 37 genes.)
 Gene therapy or gene editing couldn’t have saved Charlie, because the intervention would have to have infiltrated his many muscle and brain cells, damaged beyond repair. But could either approach enable his parents to avoid having another child with two doses of the RRM2B mutation? (Gene therapy introduces a functioning copy of a gene; gene editing can replace it.)
Gene therapy or gene editing couldn’t have saved Charlie, because the intervention would have to have infiltrated his many muscle and brain cells, damaged beyond repair. But could either approach enable his parents to avoid having another child with two doses of the RRM2B mutation? (Gene therapy introduces a functioning copy of a gene; gene editing can replace it.)
Couples who are carriers of the same recessive condition already have options to avoid passing on the disease: prenatal genetic testing to identify an affected fetus and ending the pregnancy, or preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) following IVF and selecting healthy embryos to continue development in the uterus.
Unfortunately, yesterday’s Nature paper about gene correction of a heart condition doesn’t apply to Charlie’s family. The researchers used CRISPR-Cas9 to snip a dominant mutation from sperm at the brink of fertilizing an egg, jumpstarting a natural DNA repair mechanism that copies a normal version of the gene from the egg to reconstitute two functioning copies — a little like me giving my husband a Women’s March tee-shirt to match mine and replace his Jets tee-shirt. The approach wouldn’t work for a sperm and an egg each bearing a recessive mutation in the same gene, the scenario for Charlie and 1 in 4 of his potential siblings, because there wouldn’t be a healthy gene to copy.
“It’s easier to do PGD and select those embryos that would not have a mutation in the particular gene, as is done for many other conditions,” Dr. Scaglia said. However, editing-out mutations can potentially help older women undergoing PGD by upping the percentage of okay embryos — both the number of eggs and their quality decline precipitously with age. A more pressing problem, Dr. Scaglia added, is controlling the cost of PGD and getting insurance to cover it, rather than pursuing gene editing.

[…] Source: Charlie Gard Post-Mortem: Could He Have Been Saved? […]
“Then an EEG from March 30 convinced even Dr. Hirano that an attempt at any treatment would be futile ”
What is the source for this? In the April judgement it reports that he said he had seen the EEG and it was very bad that but he still thought that there was still a (slim) chance
The family reported that it was a muscle scan in July that led him to agree treatment was futile (& that it was still not futile on July’s EEG/ MRI alone)
Thanks for the comment Sarah. The April judgement has #ed points. EEGs show electrical abnormality but not structural damage, and structural damage was the criterion for not attempting nucleoside therapy. On March 30, item 79, the MRI indeed showed no structural damage. Dr. Hirano appears in #104, in which he says the EEG was worse than he thought and uses words like “unlikely” and “terminal.” #105, still Dr. H, is more detailed, saying the damage is irreversible and nucleoside therapy wouldn’t work (this must mean brain damage). Perhaps we are both remembering further discussion in July because that’s when the pope and the president weighed in. I also remember hearing that mitochondrial DNA dipped to 1% or even less — that had to have been from a muscle biopsy, not a scan. The crucial item that I think you are referring to is #104 where the judge paraphrases Dr. H saying the probability of recovery isn’t zero, and the judge says Dr. H says that from the EEG, the brain can never be structurally normal. But the EEG doesn’t show structure, the MRI would. So the judge is mixing up EEG and MRI. He was summarizing and clearly omitting details. Reading between the lines, maybe the EEGs were abnormal all along and then the MRIs got bad. Because the TK2 patients had only muscle affected and responded to nucleoside therapy, the crucial part with Charlie was the brain, and I think that was what Dr. H was focusing on, and perhaps by July the MRI showed structural damage. I think, but am not sure, that once the EEGs and MRIs — the brain parts — were consistently bad enough, Dr. H changed his mind. Can anyone else weigh in? The judge and parents may have reported some of the medical details incorrectly.
The judge was incorrect in saying there was structural damage in April. The court of appeal specifically corrected him on that matter, but said that it did not make any difference because the evidence about the seizures showed that his neurones had died.
Charlie’s parents said that the muscle scan not the July MRI or EEG were the deciding factpr, and also Hirano is reported as saying:
“Unfortunately, a MRI scan of Charlie’s muscle tissue conducted in the past week has revealed that it is very unlikely that he would benefit from this treatment.”
He says scan not biopsy
The part I was trying to paraphrase was this part of the April judgement:
“The conversation started by Dr. I being asked whether he had seen the most recent EEG for Charlie. Dr. I confirmed that he had received the results that very morning. He said the following:
“Seeing the documents this morning has been very helpful. I can understand the opinion that he is so severely affected by encephalopathy that any attempt at therapy would be futile. I agree that it is very unlikely that he will improve with that therapy. It is unlikely.”
My point is that simply that it is unfair to say that Hirano’s mind was changed in July about evidence that existed all along.
His mind was changed by new evidence in July. So his consensus with the UK doctors in July does not prove anything about the situation in April.
It is true that his evidence in April does not give much hope for the treatment, in fact very little more hopeful than the UK doctors. Which I believe shows him to have greater credibility rather than less. He seems to have been quite honest and careful.
Thanks so much for adding this Sarah, you have more information than I do. I never meant to imply that anyone behaved unprofessionally in this very sad case. Dr. Hirano was indeed honest, careful, and of course credible. Thanks again for the clarifications. The bottom line though is that given all of the expertise involved, I think that the child was artificially ventilated for too long. However I am not a medical doctor. I’m arguing from the nature of the mutation and current limitations of nucleoside bypass. Perhaps this case will bring more attention to the challenges of treating mitochondrial diseases.
Yes, and thank you for your replies. Our disagreement might be more that you agree with the judge that Hirano’s evidence amounted to agreeing that it was futile, although he was willing to offer a treatment on the basis that it was nevertheless extremely unlikely. I guess winning the lottery is very unlikely, but not completely futile. Though I agree that ultimately it was most probably the right decision (though they may as well have just started the treatment in January and by April it would have been clear which seems to me the best)
On the broader point of the blog, would mitochondrial transfer not have been an option?
I too thought why don’t they just try it, earlier? It couldn’t have harmed him.
Alas mitochondrial transfer wouldn’t work because the mutations are on autosomes. His mitochondrial genes were ok, he just didn’t have the DNA building blocks for them to continue working. I wonder how he was able to survive birth, but he probably got the building blocks in some form through the placenta.
thanks!
The single payer system was NOT an issue. GOSH had started to investigate getting ethical permission for the experimental treatment before Charlie’s long period of seizures. After this, his brain was too damaged for any treatment to help and so they withdrew their application. If he had not had such significant brain damage, this treatment would have been administered by GOSH with input from other medics around the world regardless of cost.
Thank you for the clarification.
[…] https://blogs.plos.org/dnascience/2017/08/03/charlie-gard-post-mortem-could-he-have-been-saved/ […]